Dna Bonds With Rna Using Which Base Pair Pattern
In molecular biology two nucleotides on opposite complementary DNA or RNA strands that are connected via hydrogen bonds are called a base pair often abbreviated bp. Especially in circular DNA molecules.
They are also known as G A C and T.
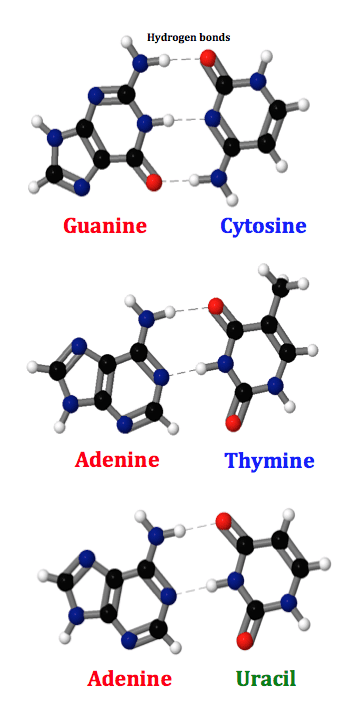
. Dipole-Dipole Interacting Bond Between two Nitrogenous Bases of the two strands of DNA. Chromosome of bacteria plasmids. Base pairs in DNA.
Adenine always bonds to thymine in DNA they are connected by two Hydrogen bonds. Due to the presence of the 2-OH hydroxyl group of ribose RNA molecules utilize an astonishing variability of base pairing patterns to build up their structures and perform the biological functions. G will only pair with either itself with C.
Thus DNA to RNA base pairing requires uracil to. In RNA thymine is replaced by uracil U. These bases always pair together in a specific way.
This is called the complementary base pairing rule or Chargaffs rule. This is observed in RNA molecules. Although very similar the base pairs in DNA and RNA differ by one nitrogenous base.
A only bonds with itself or T. The DNA molecule consists of two strands that wind around each other like a twisted ladder. In DNA uracil is.
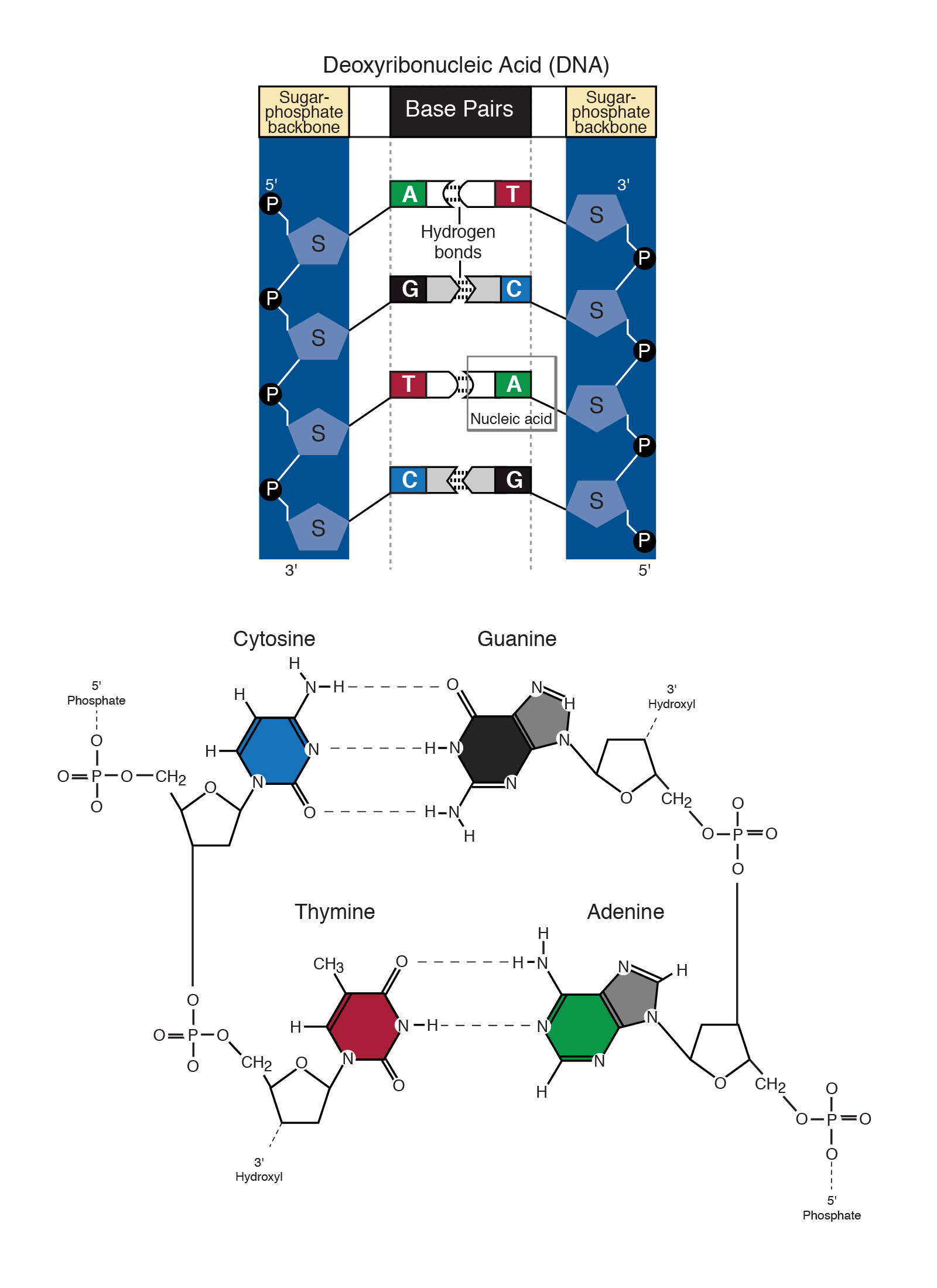
Its bonding between the nitrogenous bases that allows for this structure to form. In the canonical Watson-Crick base pairing adenine A forms a base pair with thymine T as does guanine G with cytosine C in DNA. The conversion of DNA to mRNA occurs when an RNA polymerase makes a complementary mRNA copy of a DNA template sequence.
Toward this end we report here that both a DNA and an RNA polymerase direct the incorporation of isoguanosine iso-G into an oligonucleotide opposite isocytidine iso-C in a DNA template. The chemical nature of the bases and the base pairing rules defined by experimental evidence determine the way the nucleotides interact with each other and form the structurally stable double helical DNA strands. Adenine A thymine T cytosine C and guanine G.
RNA does not contain thymine as a nitrogenous base. Watson-Crick base pairing. DNA and RNA bases are also held together by chemical bonds and have specific base pairing rules.
Adenine exclusively binds to thymine with 2 hydrogen bonds and guanine exclusively binds to cytosine with 3 hydrogen bonds. Uracil base pairs with the purine base adenine. RNA is susceptible to alkaline hydrolysis because the ribose sugar in RNA has a hydroxyl group at the 2 position which makes RNA chemically.
Cytosine and Guanine are always bonded together. Under normal circumstances the nitrogen-containing bases adenine A and thymine T pair together and cytosine C and guanine G pair together. In DNA there are four nitrogenous base options.
The base pairs of DNAs TA and CG and RNAs UA and CG need to be highly specific and accurate for the purpose of the precise genetic information storage replication transcription and translation. This is commonly known as the Base-Pair Rule. In DNARNA base pairing adenine A pairs with uracil U and cytosine C pairs with guanine G.
The phosphate groups of the DNA backbone form a zigzag pattern. In DNARNA base pairing adenine A pairs with uracil U and cytosine C pairs with guanine G. It is vice versa for the others as well.
These two molecules form a base pair with a hydrogen-bonding pattern distinct from those occurring in the natural A-TU and G-C pairs Figure 1. In DNA the four nitrogenous bases are Adenine Thymine Guanine and Cytosine. The Watson-Crick pairs are the standard DNA and RNA base pairs.
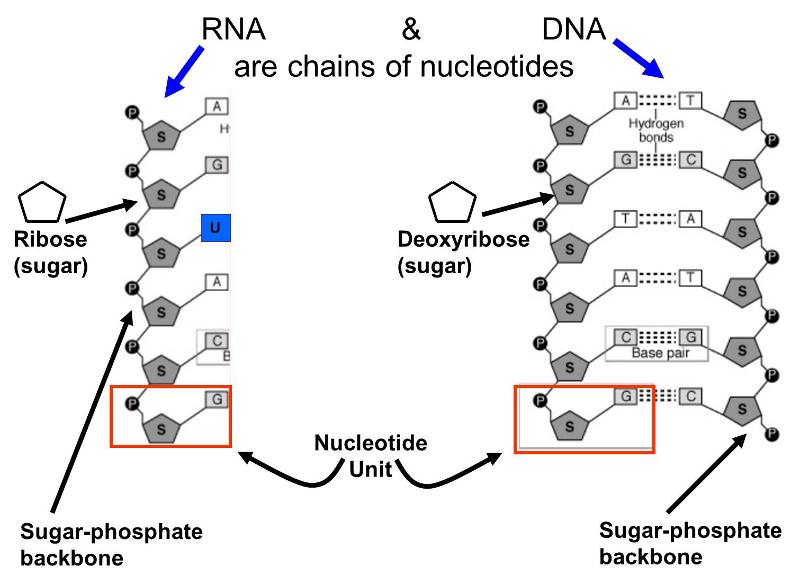
Winded double helix also termed superhelix Occurrence. Each strand has a backbone made of alternating sugar deoxyribose and phosphate groups. They are connected by three Hydrogen bonds.
The conversion of DNA to mRNA occurs when an RNA polymerase makes a complementary mRNA copy of a DNA template sequence. In this study the trans Wats. In the canonical Watson-Crick base pairing adenine A forms a base pair with thymine T as does guanine G with cytosine C in DNA.
In molecular biology two nucleotides on opposite complementary DNA or RNA strands that are connected via hydrogen bonds are called a base pair often abbreviated bp. Guanine pairs with cytosine 3 H bonds adenine pairs with thymine 2 H bonds. Why is RNA unstable.
Attached to each sugar is one of four bases--adenine A cytosine C guanine G or thymine T. In DNARNA base pairing adenine A pairs with uracil U and cytosine C pairs with guanine G. How DNA sequences itself is done by the order of these bases.
Instead RNA uses uracil to pair with adenine. The base stacking interactions are nonspecific with respect to the stacked bases and make the major contribution to the stability of the double helix. H-bonds come from the pair complementarity between DNA strands.
Two hydrogen bonds form between adenine and thymine or adenine and uracil. Guanine is the complementary base of cytosine and adenine is the complementary base of thymine in DNA and of uracil in RNA. Hydrogen Bond is a type of non-covalent bond between complementary base pairs of the DNA helix structure that shows Dipole-Dipole interactions.
Up to 24 cash back The pyrimidines are cytosine and thymine. The interaction between uracil and adenine is facilitated by a pair of hydrogen bonds. The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the bases with adenine forming.
Each nucleobase in an RNA or DNA strand chemically bonds with a complementary nucleobase on another DNA or RNA strand to form a base pair creating a double helix. DNA and RNA Base Pairing Rules DNA to DNA Possible Bases. In RNA thymine is replaced by uracil U.
DNA and RNA bases are also held together by chemical bonds and have specific base pairing rules. Adenine Thymine Cytosine Guanine GC AT A and G are purines doublering C and T are pyrimidines singlering DNA to mRNA Possible Bases. Adenine pairs with thymine or uracil while guanine pairs with cytosine.
DNA and RNA bases are also held together by chemical bonds and have specific base pairing rules. Each base can only bond with one other A with T and C with G. Adenine Thymine Cytosine Guanine Uracil RNA only.
The same pairs apply to RNA except that uracil replaces thymine. Terms in this set 11 either of the nucleotide bases linked by a hydrogen bond on opposite strands of DNA or double-stranded RNA. Which RNA base pairs with the adenine in DNA thymine guanine cytosine uracil quizlet.
These bonds are very weak and non-covalent bonds but provide great stability to the structure. The pattern of repeating units creates a sequence in which genetic information can be stored. The binding of these base pairs forms the structure of DNA.
Many of the key RNA base pairing families have no counterparts in DNA. In DNA adenine bonds to thymine while guanine bonds with cytosine. A bonds with U in RNA G bonds with C in DNA RNA DNA base pair.
Uracil and thymine molecules are very similar in shape allowing them to form the same kinds of hydrogen bonds with adenine. However the wobble base pairs where U in RNA or T in DNA pairs with G instead of A may compromise the high specificity of the base pairing.

0 Response to "Dna Bonds With Rna Using Which Base Pair Pattern"
Post a Comment